Considered to be a major milestone in the history of Indian banking, Cheque Truncation System (CTS) aims to make cheque clearance more efficient and reduce the clearance time of cheques to one day, thereby trimming down the floating time considerably. India processes as many as 1.2 billions cheques annually and therefore, the implementation of this system would drastically cut down the waiting period involved. The system will be implemented nationwide from April 1, 2013.
Impact of CTS on Customers
Handling of EMIs with the Introduction of CTS
In cases where customers have issues post-dated cheques (PDC) for payment of monthly installments towards an ongoing loan, they would need to issue fresh cheques to the bank or service provider as per the new directive on CTS by the RBI. The replacement of these cheques needs to be done latest by April 1, 2013 and is applicable on all banks and NBFCs.
Encashment of Old Cheques
Customers may need to surrender their old cheque books or cancel them and show proof of cancellation. No replacement fee will be charged by the bank for issuing new cheque books
Apart from these aspects, the system does not, in any way, affect the way things function for a customer. They would continue using cheques as they do currently; however, cheques that have been altered or modified will not be permissible under the new system. The other precautions that need to be taken while issuing or writing a cheque are:
Benefits of CTS for Customers
There are many benefits of the cheque truncation system from the perspective of a customer.
How does it work?
An online image-based cheque clearing system, the collecting bank branch would deploy scanned images along with the magnetic ink character (MICR) of the cheque which will be sent out electronically using their Capture System, removing the need for physical/manual transfer of cheques. The captured images and the data is then signed and encrypted and sent to the Clearing House or the central processing location and thereafter forwarded to the drawee or paying bank.
This helps speed up the cheque collection process that eventually helps provide better and faster customer service.
Key Features of Cheque Truncation System
An online image-based cheque clearing system, the collecting bank branch would deploy scanned images along with the magnetic ink character (MICR) of the cheque which will be sent out electronically using their Capture System, removing the need for physical/manual transfer of cheques. The captured images and the data is then signed and encrypted and sent to the Clearing House or the central processing location and thereafter forwarded to the drawee or paying bank.
This helps speed up the cheque collection process that eventually helps provide better and faster customer service.
Key Features of Cheque Truncation System
- User friendly graphic user interface
- Automated coding and endorsing of cheques
- Encryption of data file before transmission to the clearing house or the service branch
- Employs a unique transaction follower process to confirm the status of cheque
- Improved and efficient settlement and prevention of fraud
- Equipped with enhanced archival procedure that stores images and data facilitating report generation along with future enquiry
- Alerts RMs in case of return of cheque due to insufficient funds
Impact of CTS on Customers
Handling of EMIs with the Introduction of CTS
In cases where customers have issues post-dated cheques (PDC) for payment of monthly installments towards an ongoing loan, they would need to issue fresh cheques to the bank or service provider as per the new directive on CTS by the RBI. The replacement of these cheques needs to be done latest by April 1, 2013 and is applicable on all banks and NBFCs.
Encashment of Old Cheques
Customers may need to surrender their old cheque books or cancel them and show proof of cancellation. No replacement fee will be charged by the bank for issuing new cheque books
Apart from these aspects, the system does not, in any way, affect the way things function for a customer. They would continue using cheques as they do currently; however, cheques that have been altered or modified will not be permissible under the new system. The other precautions that need to be taken while issuing or writing a cheque are:
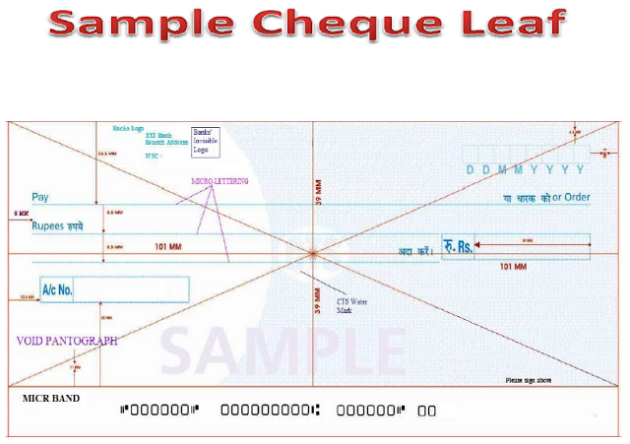
- Ensure that all details are clear and readable, using black or blue ink
- Write the name of the payee, amount and the date and sign the cheque correctly.
- In case you use seals on the cheque, ensure that they are imprinted in a manner that they do not mask or hide the other important fields of the cheque.
Benefits of CTS for Customers
There are many benefits of the cheque truncation system from the perspective of a customer.
- Clearance cycle gets shortened - As this system is being implemented, the physical or manual movement of cheques for clearance has ceased. With cheques being transmitted electronically, the settlement process becomes quicker, facilitating reduction in the clearance cycle.
- The fear of loss of cheques during transfer from the collecting bank to the drawee or payee bank is eliminated.
- Limitations of the current clearance system with respect to jurisdiction and geography are eradicated. This enables integration and consolidation of several clearing locations across various banks offering different service levels into one standard clearance system applicable throughout the country.
- CTS helps reduce the scope of fraud significantly. Moreover, the electronic transmission is quick and allows early detection of fraud or any alteration with respect to the payee, amount or the issuer of the cheque. CTS prescribe minimum security features under ‘CTS-2010 standards’ along with superior verification process that further facilitates in the reduction of frauds.
- The operational efficiency of both the bank as well as the customer is enhanced with the introduction of this system.